

What Is Assimilation In Phonological Rules? Backing. Phonological processes typically begin to disappear, or are suppressed by the age of four. However, developmental speech-sound norms differ in age and gender for each speech sound and cluster. cluster reduction, initial consonant deletion, reduplication, weak syllable deletion, final consonant deletion, epenthesis. In this episode of the Speech and Language Kids Podcast, I will teach you about phonological processes and phonological disorders. What is Vowelization phonological process? Deaffrication is the substitution of a nonaffricate sound for … Phonological processes examples. This also involves two processes: deletion of the initial cluster ‘spl-’. fronting of the final back sound ‘k’ to the front sound ‘t’. Simplify speech as they are learning to talk. A fricative sound like /f/ or /s/ or affricate sound like “ch” or “j” is substituted with a stop consonant like /p/ or /b/. Patterns of Phonological Processes in Spanish‐English Bilingual Children Ellen Stubbe Kester Scott Prath NovemASHA, Denver. The research design used in this study can teach us about the development of the reading process when there is short vowelization, when taking different kinds of texts and genres into consideration. Denasalization – the substitution of a nasal consonant (“n†or “m†) with a non-nasal consonant (“b†or “d†) - When velar or palatal sounds, like /k/, /g/, and sh, are substituted with alveolar sounds like /t/, /d/, and /s/ When a nonaffricate is replaced with an affricate (ch or j) Fronting Affrication “tootie” for “cookie” “joor” for “door” Danville, IL. It is more likely to undergo a process known as vowelization. Substitution Processes Fronting: substitute a sound formed in the back of the mouth with an anteriorly produced sound (ex: /t/ for /k/) Stopping: substitution of a stop sound for a fricative or affricate … jump → dump) Between 3 and 5 years of age. Cluster reduction The effect of target-selection strategy on phonological learning. This process will disappear by the age of 3. The phonology of a sociocultural variety: The case of African American Vernacular English. The chapter describes the mainstream analysis for BP and EP nasal vowels, which derives these sounds from an underlying/VN/sequence. A bilabial labio-dental dental alveolar post-alveolar or palatal consonant is substituted by.

These are considered natural or normal phonological processes. In contemporary EP, this process is inoperative. Phonological!processes!arepredictablepatterns!that!all!children!use!to!simplifyspeech!astheyare!learning!totalk. Assimilation processes: when sounds/syllables start to sound like surrounding sounds. Phonological processes are patterned speech sound errors. Vocalization (voc), also called Vowelization, is a phonological process which typically starts to assimilate around the age of 3.5 years, and sometimes lasts up to the age of 5-7 years. Terms in this set (43) surprise → /praɪz/ weak syllable deletion.
#Phonological processes age of elimination manual
This process is the latest to be eliminated from a child’s speech in typical development, and because of this, as well as the involvement of the pesky /r/ sound (very complex in itself), this … A manual analysis was done on the other 26 phonemic substitutions, assimilations, voicing alterations, and TABLE 2: Phonological Processes in Typical Speech Development PHONOLOGICAL PROCESS (Phonological Deviation) EXAMPLE DESCRIPTION These are formed by the arrangement of a nucleus (vowel), and a coda (the final consonant). Since 1998 has provided information and resources to Speech-Language Pathologists / Speech and Language Therapists (SLPs/SLTs), students, consumers of SLP/SLT services worldwide, and interested others. We should no longer hear this process after the age of 3.
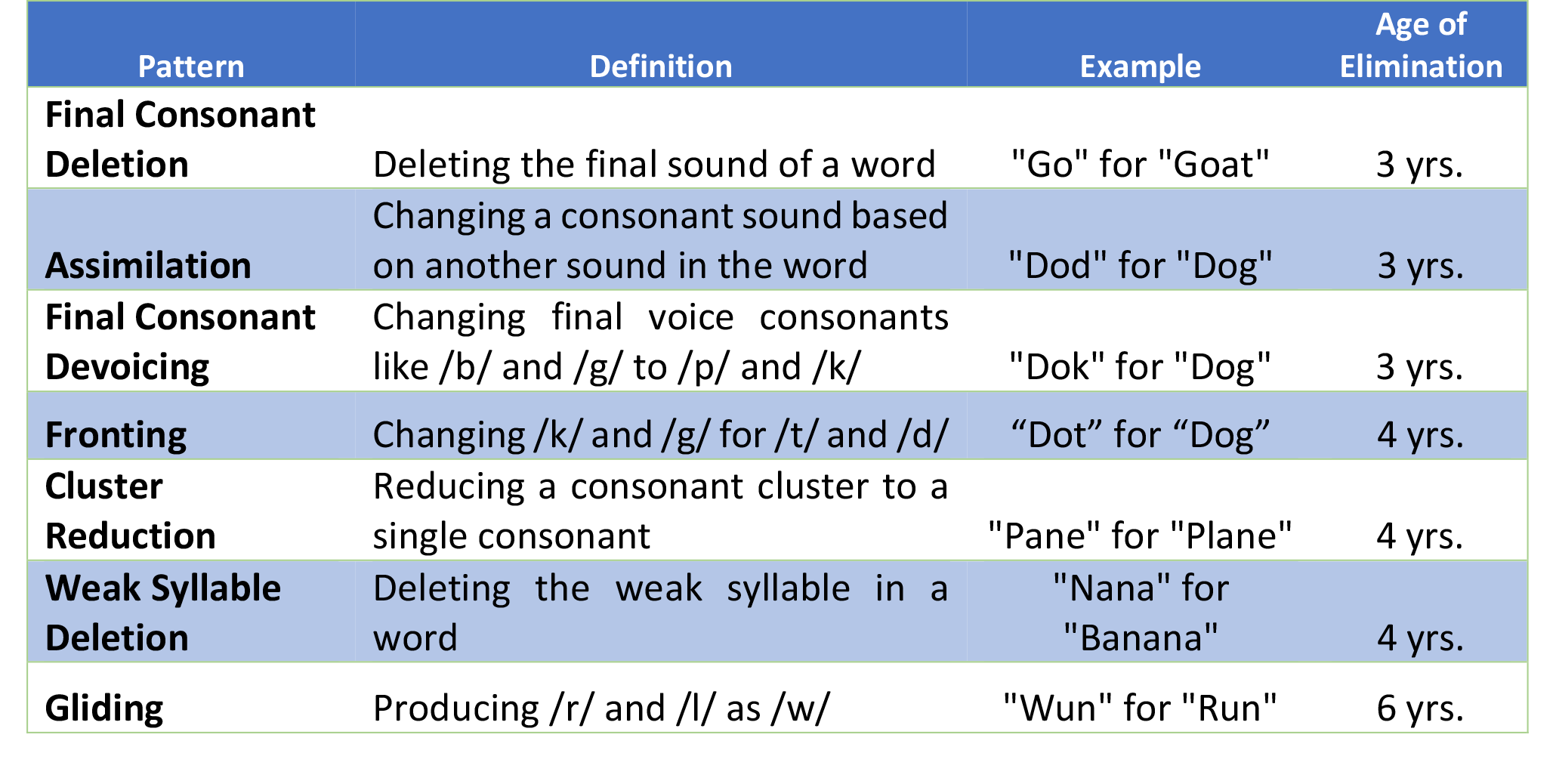
It is not a complete list for more information, please contact your SLP. Phonological Processes-Revised (APP-R) (Hodson, 1986) was administered to both groups. Backing is a common phonological process. Número 2: Phonological Processes are largely shared. Every preschooler needs to grasp the following goals to master phonological awareness: Rhyming: identification of a sequence of words where there is regular recurrence of similar words, mostly at the ends. The change may be in the # of syllables or in the shape of syllables. This is not a phonological unit but an abstract entity. , Stopping, Gliding, Lateral realization, of apical and coronal fricatives, Vowelization of /l/, and /r/. Phonological processes for non-target consonants and vowels included affrication ch/t (e., cheeth/teeth), typically suppressed at age 3, and vowelization a/r (e., zippa/zipper),typically supporessed at age 4. This is when a liquid consonant in syllable-final position is replaced with a vowel, e.g.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
